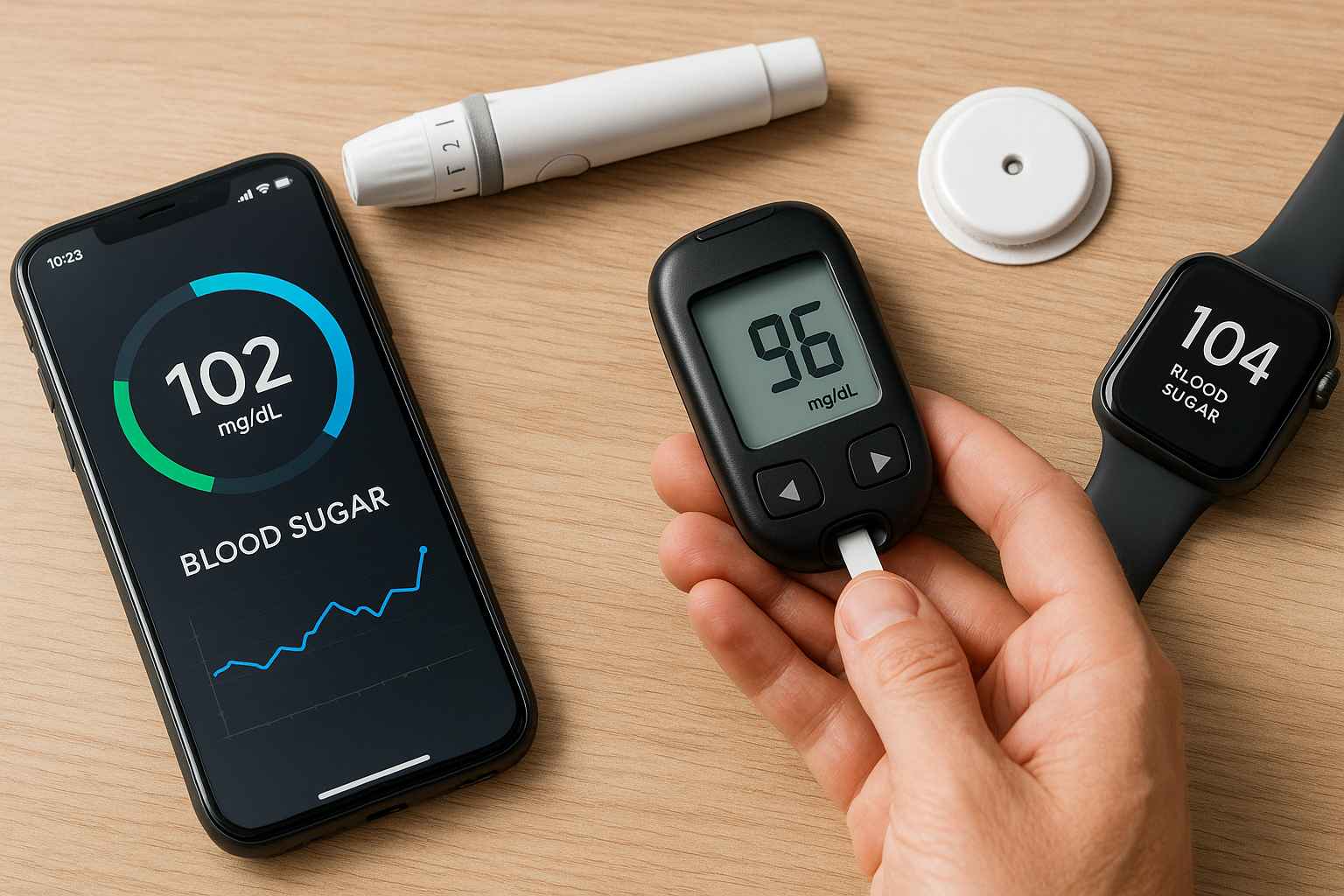
Signs of high blood sugar can include excessive thirst and hunger, increased urination, and fatigue.
Hyperglycemia, or elevated blood sugar, often develops slowly, with subtle early symptoms such as fatigue and increased thirst that may go unnoticed for years. If left unmanaged, persistent high blood sugar can damage blood vessels and lead to serious complications involving the eyes, heart, kidneys, and feet.
01: Thirst That Won’t Quit: Early Warning Sign of Diabetes

Your kidneys play a key role in managing blood sugar by filtering and reabsorbing glucose, which is why normal urine contains little to no sugar. When blood sugar levels become too high, the kidneys are forced to work harder to eliminate the excess. To do this, they draw fluids from body tissues to help flush out the sugar through urine, leading to dehydration. As a result, you may experience persistent dry mouth or intense thirst that doesn’t go away, no matter how much you drink—an important warning sign of hyperglycemia.
02: Urinating More Than Usual: A Hidden Symptom of High Blood Sugar

More frequent urination, particularly at night, can be an early sign of high blood sugar. This occurs when the kidneys pull additional water from body tissues to help dilute and remove excess glucose from the bloodstream, resulting in increased urine production.
03: Unusual Cravings: A Sign of Blood Sugar Imbalance

When excess sugar builds up in your bloodstream, it means your body isn’t able to use it efficiently for energy. As a result, your cells are deprived of fuel, triggering increased hunger. This can lead to eating more in an attempt to satisfy that energy need. However, your food choices matter—consuming more carbohydrates can further spike your blood sugar, worsening the problem.
04: Blurry Vision: A Subtle Symptom of Rising Blood Sugar

High blood sugar levels cause the body to draw fluid from tissues, including the lenses of your eyes. This shift in fluid can alter the shape of the lenses, making it harder to focus clearly and resulting in blurry vision.
05: Constantly Tired? Your Blood Sugar Might Be to Blame

Under normal conditions, your cells absorb blood sugar to produce energy. But when glucose remains in the bloodstream instead of entering your cells, they’re left without the fuel they need. This energy shortage can leave you feeling sluggish or fatigued—particularly after eating a high-carb meal, which further elevates blood sugar levels.
06: Itchy, Dry, or Discolored Skin? It Could Be a Sign of Diabetes
Dry, itchy skin and slow-healing cuts or wounds can be indicators of high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia). Another potential sign of insulin resistance is acanthosis nigricans—a condition where dark, thick, velvety patches appear in body folds or creases, such as around the neck.
07: When Infections Keep Coming Back: A Sign of High Blood Sugar
When blood sugar levels are high, your immune system may become compromised, making you more susceptible to infections. Some types of bacteria even thrive in high-sugar environments, allowing them to multiply more easily in the body. Additionally, yeast feeds on sugar—so elevated blood sugar can lead to yeast overgrowth. This is why individuals with vaginas may experience frequent yeast infections when their blood sugar remains high.
08: How Elevated Blood Sugar Can Disrupt Your Mood and Mental Clarity

Researchers believe that blood sugar levels may influence mood. Although more studies are needed, some evidence suggests that elevated post-meal blood sugar in individuals with type 2 diabetes may be associated with negative mood symptoms, such as irritability. Other research has also linked higher blood sugar levels to increased feelings of anger and sadness in people with diabetes.
09: Why High Blood Sugar Might Be Causing Your Stomach Pain
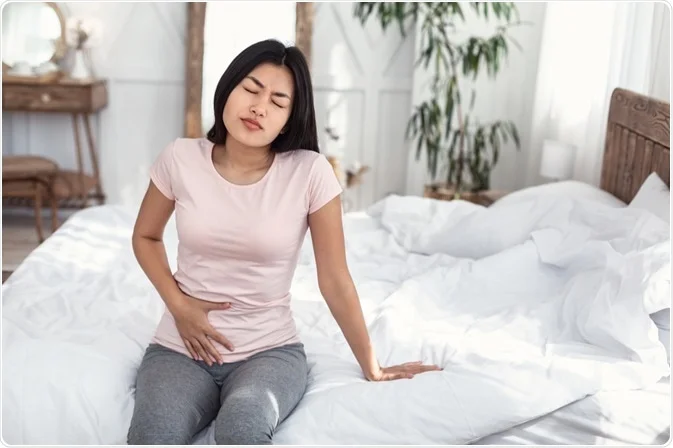

Consistently high blood sugar levels (chronic hyperglycemia) can damage the nerves in the stomach, leading to a condition called gastroparesis, or delayed gastric emptying. This can result in symptoms like nausea and sluggish digestion. Additionally, stomach pain may signal diabetic ketoacidosis—a serious and potentially life-threatening complication that requires immediate medical attention.
10: Silent Signals: Numbness and the Hidden Nerve Damage of Diabetes
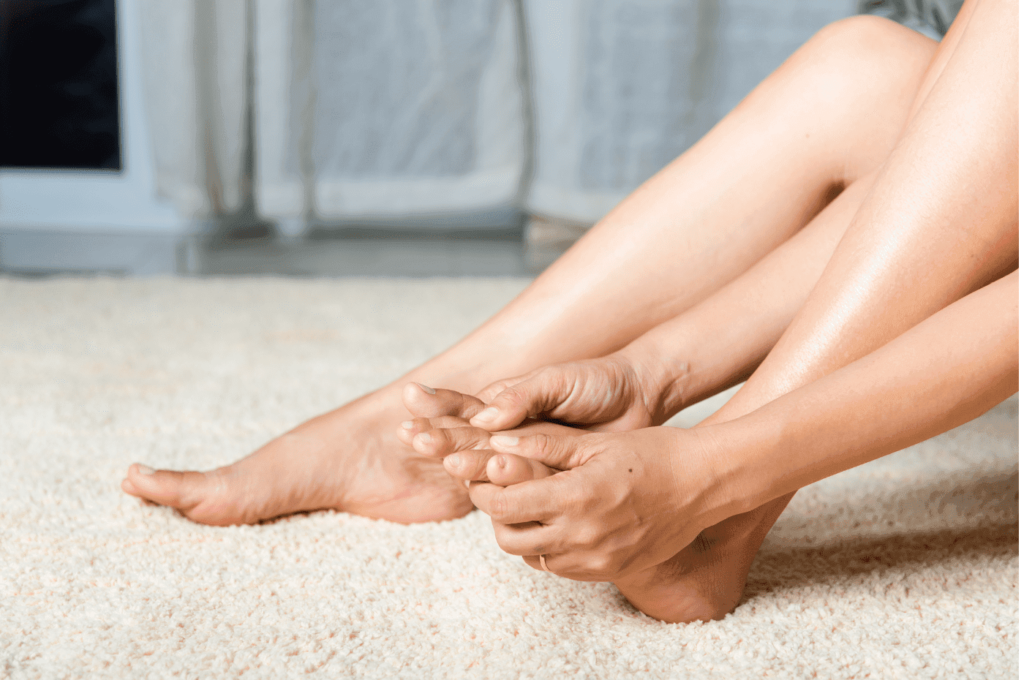

Persistent high blood sugar can damage nerves throughout the body, a condition known as diabetic neuropathy. This often begins as a tingling or burning sensation and may progress to numbness, typically in the hands, feet, or legs. Left unmanaged, this nerve damage can affect balance, increase the risk of injury, and reduce sensitivity to pain or temperature changes.
11: Silent Signals: What Unintended Weight Loss Could Mean for Your Health

Unintentional weight loss can be an early warning sign of high blood sugar, especially in children who are frequently thirsty and urinating often. In many cases, kids with type 1 diabetes lose weight before diagnosis because their bodies are unable to use glucose for energy.
Why Early Detection Matters:
KEY TAKE-AWAYS
What Can Happen with Long-Term High Blood Sugar?
When blood sugar stays too high for too long (a condition called chronic hyperglycemia), it can cause serious health problems. These problems affect both small and large blood vessels throughout the body.
Problems with Small Blood Vessels (Microvascular Complications)
High blood sugar can damage tiny blood vessels, leading to:
- Eye problems (retinopathy) – Can cause blurry vision or even blindness.
- Kidney damage (nephropathy) – Can lead to kidney failure if not treated.
- Nerve damage (neuropathy) – Can cause numbness, pain, or tingling in the feet and hands. It can also affect digestion, bladder control, and other body functions.
Problems with Large Blood Vessels (Macrovascular Complications)
Larger blood vessels can also be damaged, raising the risk for:
- Heart disease – Including heart attacks and strokes.
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD) – A condition where poor blood flow causes pain or cramping in the legs, especially when walking.
Other Serious Health Issues
- HHNKC (Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Coma)
Most common in people with type 2 diabetes, this is a medical emergency. Blood sugar gets extremely high (over 600 mg/dL), causing symptoms like confusion, extreme thirst, fever, weakness, or even paralysis. If not treated, it can lead to coma or death. - DKA (Diabetic Ketoacidosis)
More common in people with type 1 diabetes, this happens when the body doesn’t have enough insulin. It causes high blood sugar and acid buildup in the blood. Symptoms include extreme thirst, frequent urination, nausea, and rapid breathing. DKA needs immediate medical care. - Erectile Dysfunction
High blood sugar can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to sexual problems in men. - Pregnancy Complications
Poor blood sugar control during pregnancy can raise the risk of:- Miscarriage
- High blood pressure (preeclampsia)
- Low blood sugar in newborns
Doctors recommend aiming for an A1C level below 6.5% before getting pregnant.

