
Bananas are a nutrient-dense superfood, packed with potassium, fiber, and natural sugars—but can you have too much of a good thing? While bananas support heart health, digestion, and energy levels, overconsumption may lead to digestive distress, blood sugar spikes, and even heart rhythm issues.
In this evidence-based guide, we’ll explore:
✔ 7 unexpected side effects of excessive banana intake
✔ How many bananas per day is safe? (Portion control tips)
✔ Best ways to eat bananas for optimal digestion & blood sugar balance
✔ Healthy banana alternatives (For variety & nutrient diversity)
Let’s peel back the truth! 🍌
7 Side Effects of Eating Too Many Bananas
1. Digestive Issues (Bloating, Gas & Constipation)

Bananas are rich in soluble fiber (pectin) and resistant starch, which can cause:
- Bloating & gas (Due to fermentation in the gut)
- Constipation (Unripe bananas contain tannins that slow digestion)
- Diarrhea (Overripe bananas have high sorbitol, a natural laxative)
Fix: Stick to 1-2 ripe bananas daily and pair with probiotic foods (yogurt, kefir) for better digestion.
2. Blood Sugar Spikes & Insulin Resistance
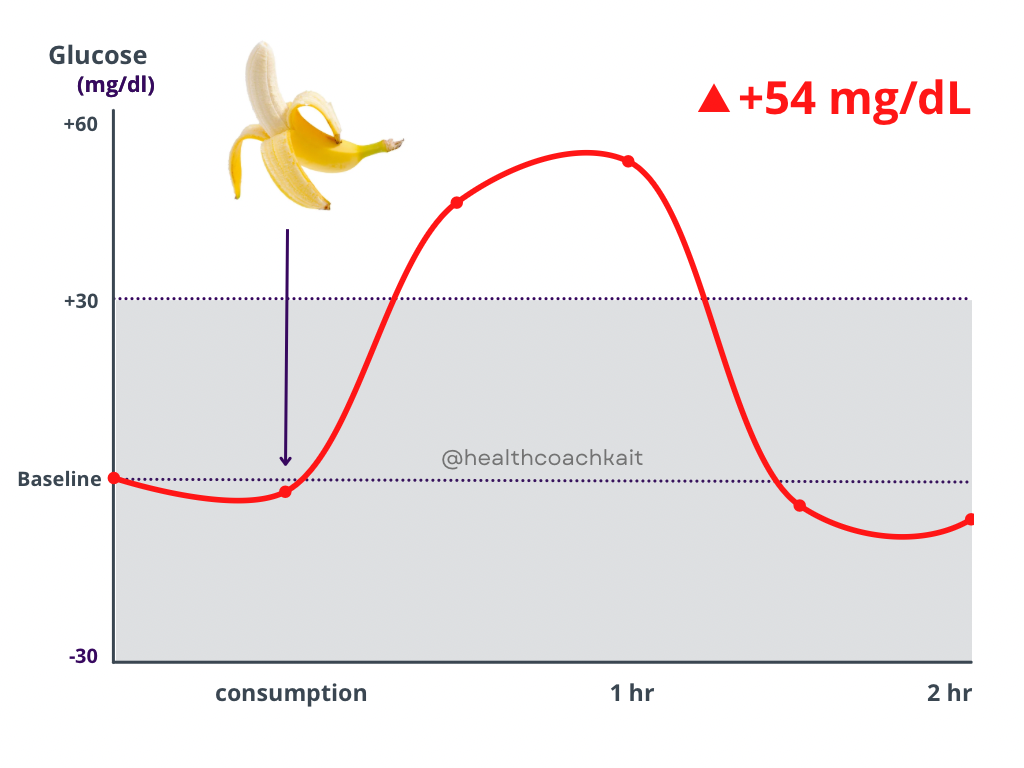
While bananas have a moderate glycemic index (GI 51), eating too many can spike blood sugar due to:
- High fructose & glucose content (14-20g sugar per banana)
- Rapid carb absorption (Especially in overripe bananas)
Risk: May worsen prediabetes or metabolic syndrome if consumed in excess.
Fix: Opt for firm, slightly green bananas (lower GI) and pair with protein (nuts, Greek yogurt) to slow sugar absorption.
3. Weight Gain (Hidden Calorie Trap)
A medium banana has ~105 calories—eating 3-4 daily adds up quickly. Excess calories from bananas (without exercise) can lead to fat storage, especially around the abdomen.
Fix: Balance banana intake with high-protein, high-fiber meals to stay full longer.
4. Hyperkalemia (Dangerous Potassium Overload)

Bananas are famous for potassium (422mg per banana), but too much can cause:
- Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia)
- Muscle weakness
- Nausea & tingling sensations
At-risk groups: People with kidney disease or on potassium-sparing medications.
Fix: Limit to 1 banana/day if you have kidney issues.
5. Nutrient Imbalances (Missing Key Vitamins)
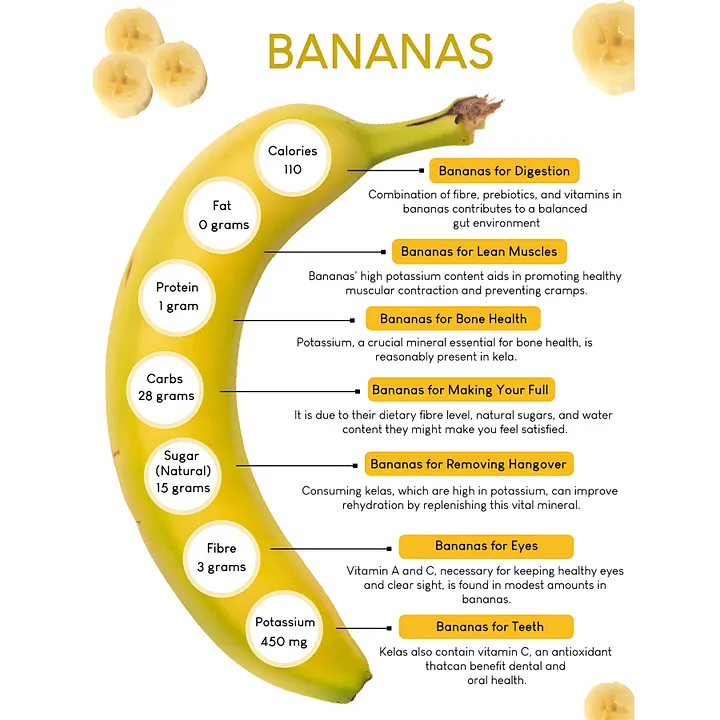
Relying only on bananas may lead to deficiencies in:
- Vitamin D, B12, Iron, Zinc (Not found in bananas)
- Healthy fats & complete proteins
Fix: Diversify with berries, leafy greens, nuts, and lean proteins.
6. Tooth Decay (Natural Sugars & Sticky Texture)
Bananas contain natural sugars that feed oral bacteria, increasing risk of:
- Cavities
- Enamel erosion (Due to mild acidity)
Fix: Rinse mouth with water after eating or chew sugar-free gum.
7. Rare Banana Allergies (Latex-Fruit Syndrome)
Some people allergic to latex may react to bananas due to chitinase proteins, causing:
- Itchy mouth/throat
- Hives or anaphylaxis (in severe cases)
Fix: Avoid bananas if you have a latex allergy and consult an allergist.
How to Eat Bananas Safely: Nutrition & Portion Control
✅ Safe Banana Intake Per Day
| Group | Recommended Daily Limit |
|---|---|
| Healthy Adults | 1-2 medium bananas |
| Athletes/Active Individuals | 2-3 (for quick energy) |
| Diabetics/Prediabetics | ½-1 (with protein/fat) |
| Kidney Disease Patients | ½-1 (monitor potassium) |
✔ Best Ways to Eat Bananas for Optimal Health
- Pair with Protein/Fat (Peanut butter, almonds, chia seeds) → Slows sugar absorption.
- Choose Slightly Green Bananas → Higher resistant starch, lower GI.
- Blend in Smoothies (With spinach, flaxseeds, protein powder) → Balanced nutrition.
- Bake or Freeze → Reduces glycemic impact vs. raw.
❌ When to Avoid Bananas
- If you have IBS (May trigger bloating)
- Latex allergy sufferers
- Post-workout (alone) → Can cause sugar crash.
5 Healthy Banana Alternatives
If you’re cutting back, try these low-sugar, high-fiber options:
- Berries (Blueberries, raspberries) → Lower sugar, high antioxidants.
- Apples + Nut Butter → More fiber, less glycemic spike.
- Avocados → Healthy fats, creamy texture.
- Sweet Potatoes → More vitamin A, slower-digesting carbs.
- Kiwi → Higher vitamin C, aids digestion.
FAQs: Your Banana Questions Answered
1. Can bananas cause stomach problems if eaten in excess?
Yes! Too many bananas can cause bloating, gas, or constipation due to high fiber and resistant starch. Stick to 1-2 per day and drink plenty of water.
2. How many bananas are too many in a day?
- Healthy adults: Max 2-3 (if very active).
- Diabetics/Kidney patients: ½-1 max.
3. What are the best banana alternatives?
Try berries, apples, kiwis, or avocados for similar nutrients without the sugar overload.
4. Can bananas help regulate blood sugar?
Only in moderation! Slightly green bananas (higher resistant starch) are better for blood sugar than overripe ones.
5. Are bananas good for heart health?
Yes—in moderation! Potassium supports blood pressure, but too much can harm those with kidney issues.
Final Verdict: Are Bananas Healthy?
Bananas are a nutrient-packed snack, but balance is key. Stick to 1-2 per day, pair with protein/fat, and diversify your fruit intake for optimal health.
Want more science-backed nutrition tips? Subscribe to our newsletter for weekly wellness insights! 🌿

